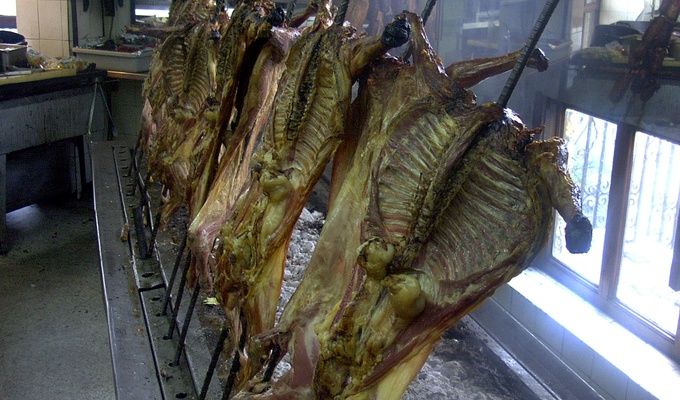
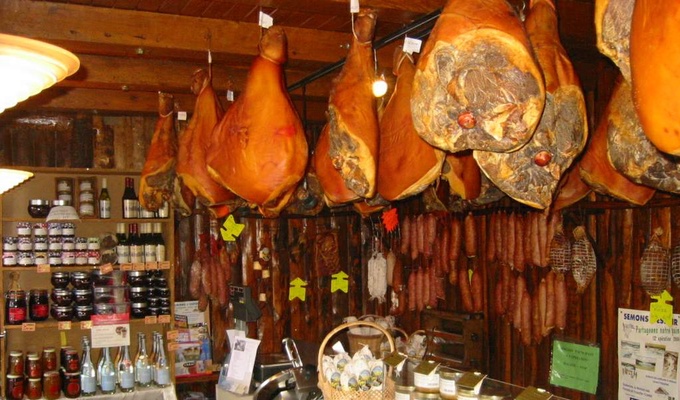
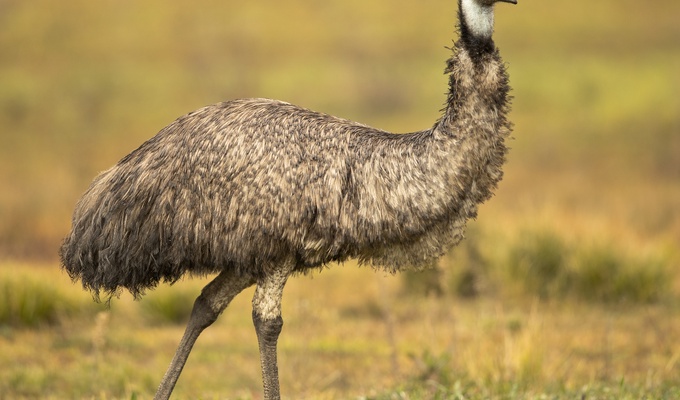
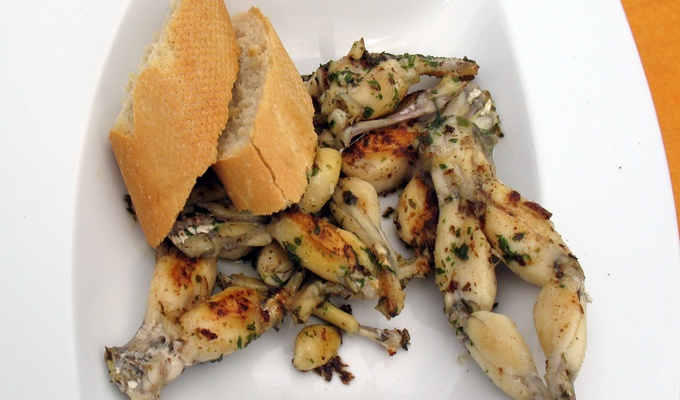
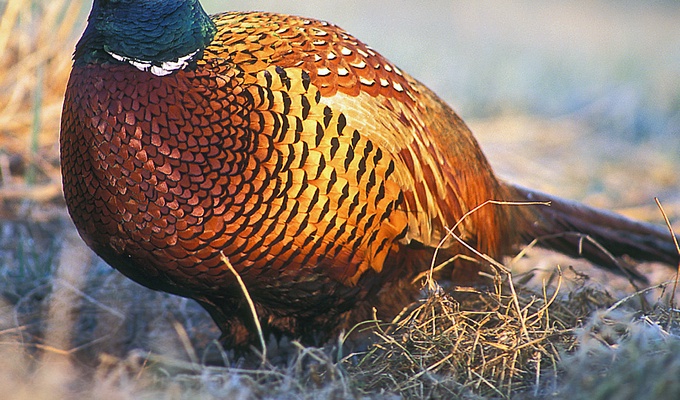
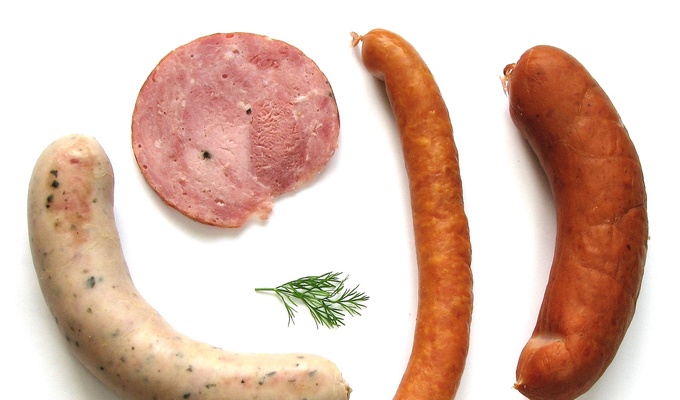
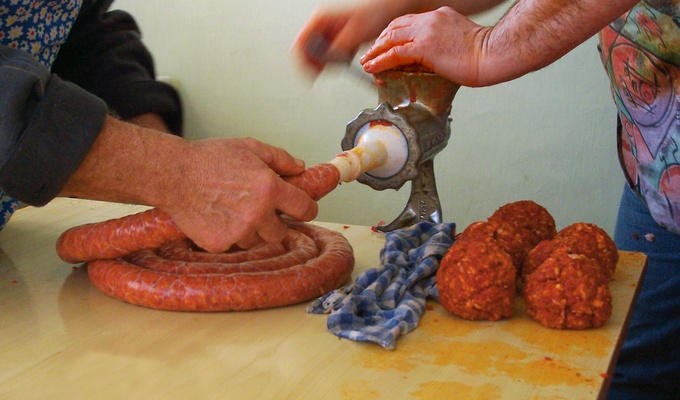
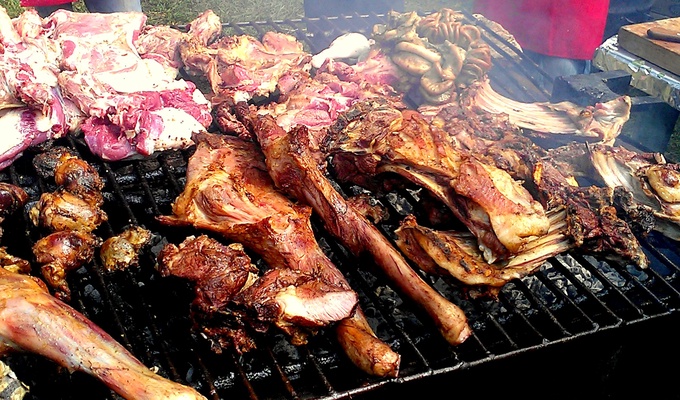
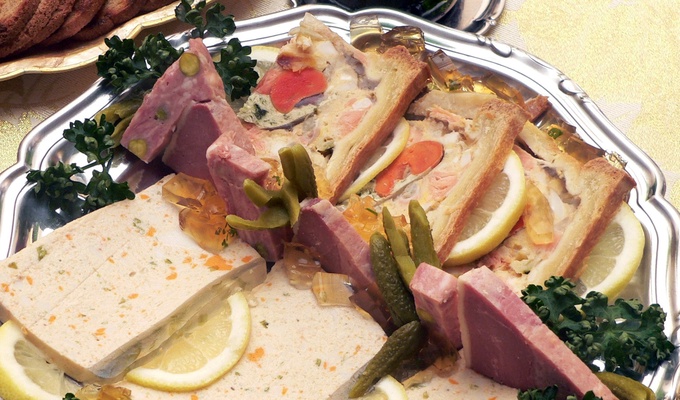
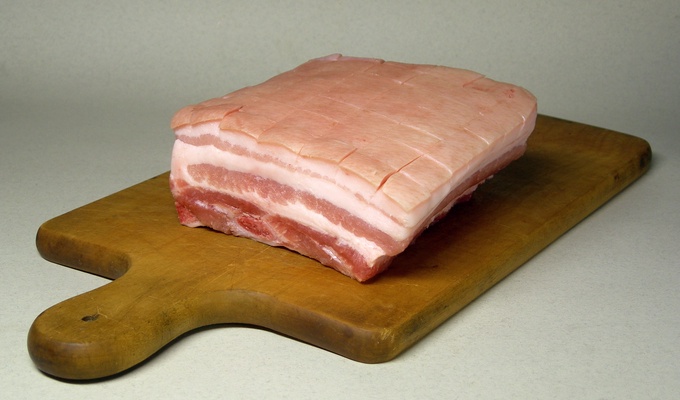
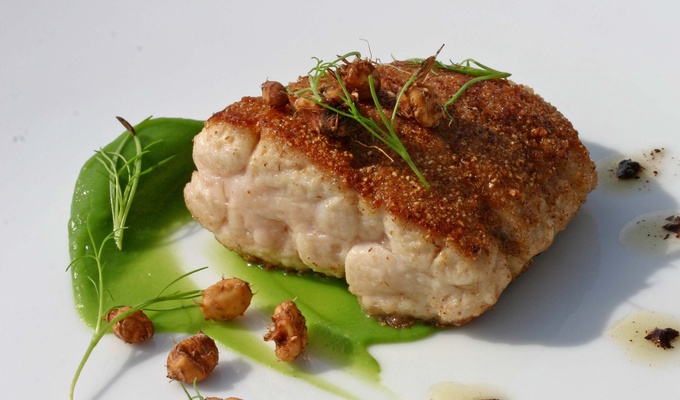
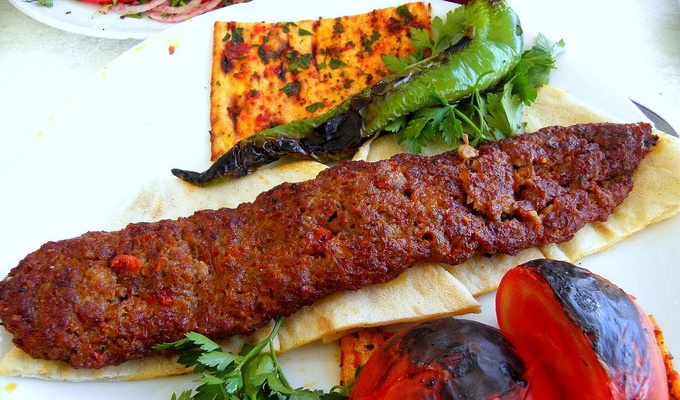
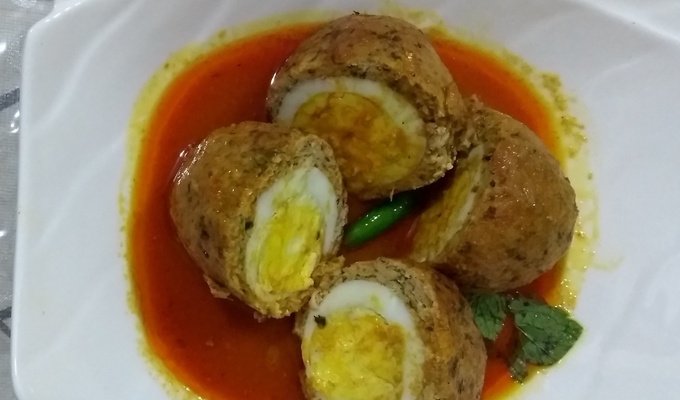
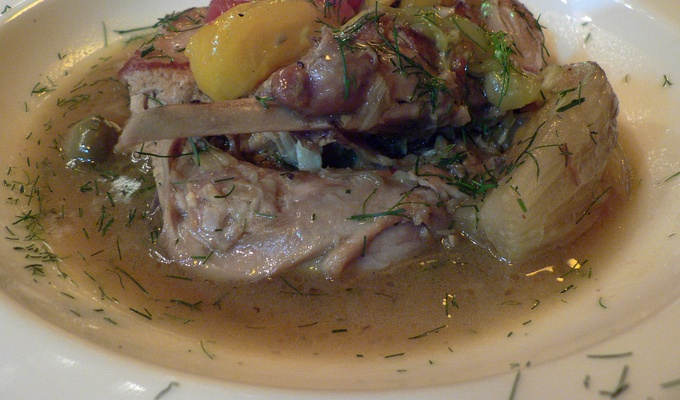
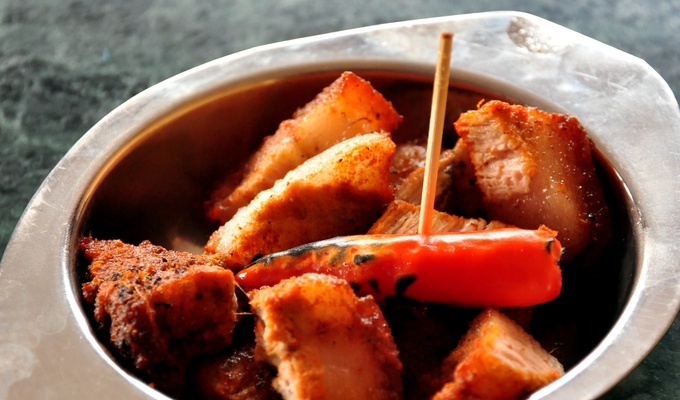
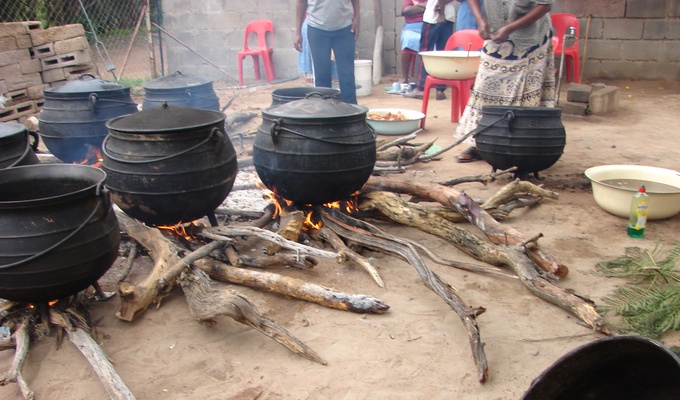
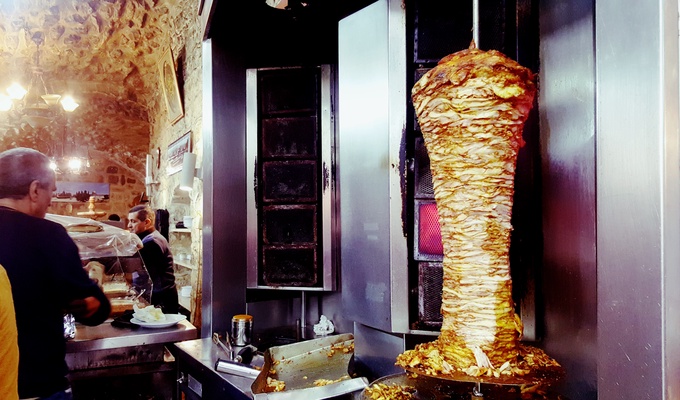
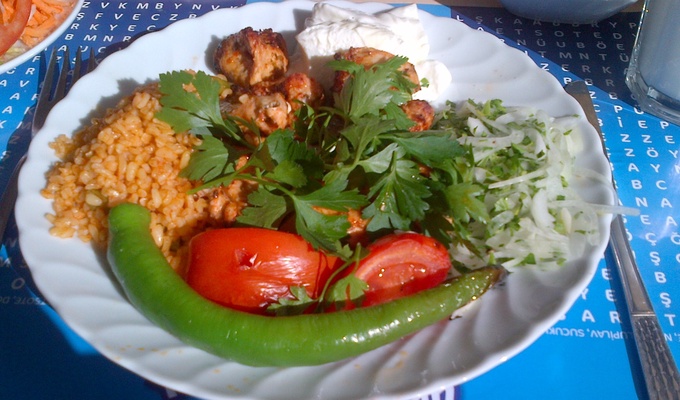
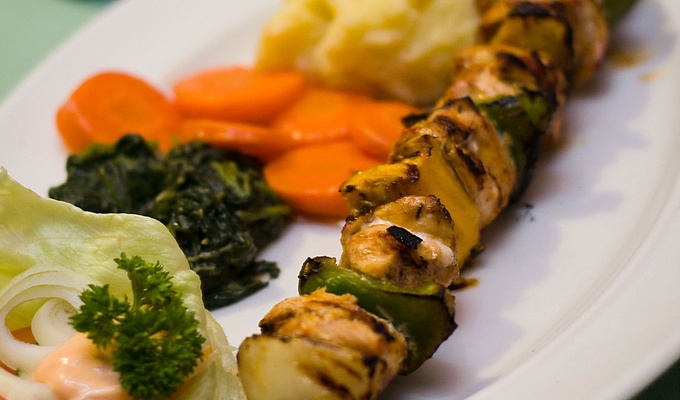
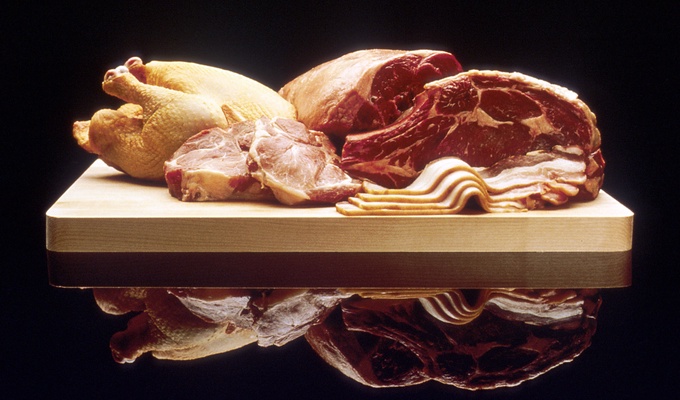
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chickens, sheep, rabbits, pigs, and cattle. This eventually led to their use in meat production on an industrial scale in slaughterhouses.
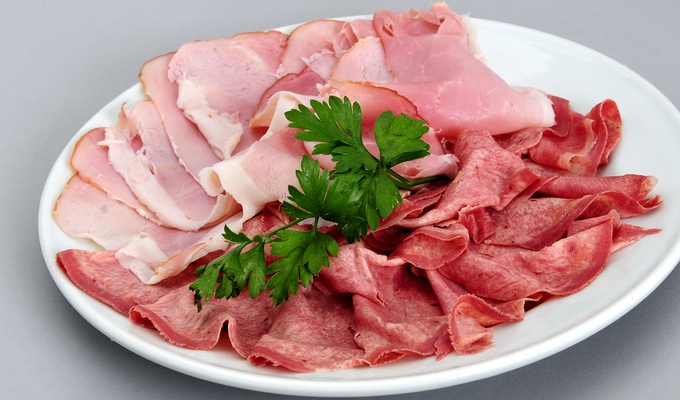
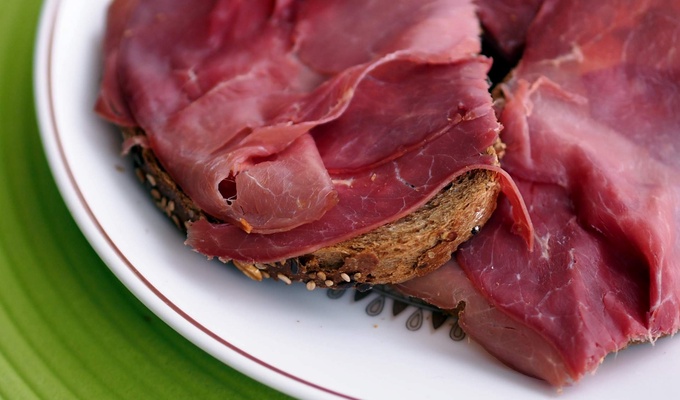
Meat is mainly composed of water, protein, and fat. It is edible raw, but is normally eaten after it has been cooked and seasoned or processed in a variety of ways. Unprocessed meat will spoil or rot within hours or days as a result of infection with, and decomposition by, bacteria and fungi.
Meat is important to the food industry and to economies and cultures around the world. There are nonetheless people who choose to not eat meat (vegetarians) or any animal products (vegans), for reasons such as taste preferences, ethics, environmental concerns, health concerns or religious dietary rules.