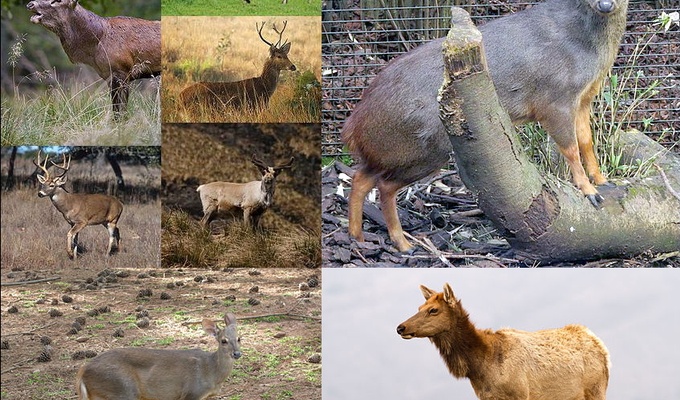
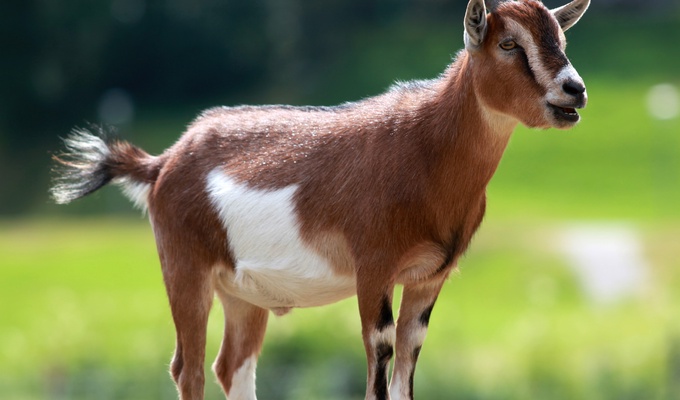
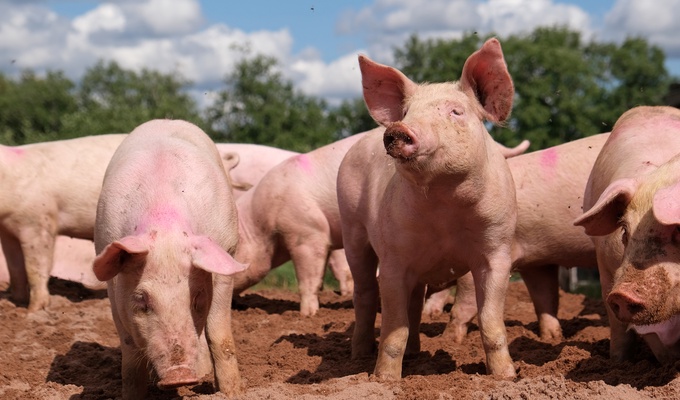
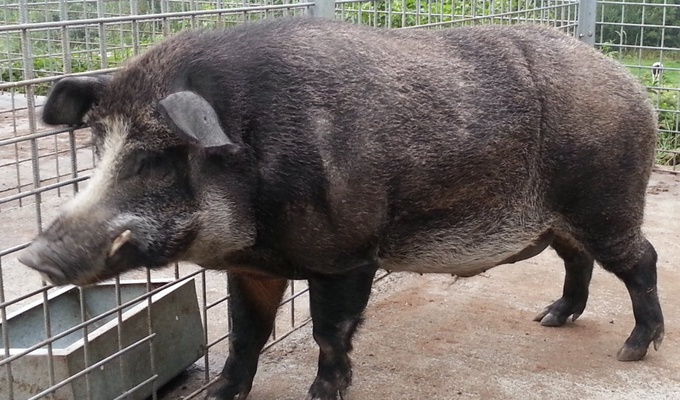
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce commodities such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals who are raised for consumption, and sometimes used to refer solely to farmed ruminants, such as cattle, sheep, goats and pigs. Horses are considered livestock in the United States. The USDA classifies pork, veal, beef, and lamb as livestock, and all livestock as red meat. Poultry and fish are not included in the category.
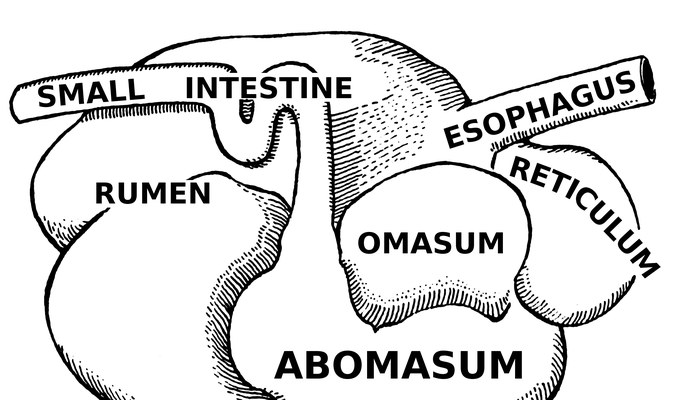
The breeding, maintenance, slaughter and general subjugation of livestock, called animal husbandry, is a part of modern agriculture and has been practiced in many cultures since humanity's transition to farming from hunter-gatherer lifestyles. Animal husbandry practices have varied widely across cultures and time periods. It continues to play a major economic and cultural role in numerous communities.
Livestock farming practices have largely shifted to intensive animal farming. Intensive animal farming increases the yield of the various commercial outputs, but also negatively impacts animal welfare, the environment, and public health. In particular, beef, dairy and sheep are an outsized source of greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture.