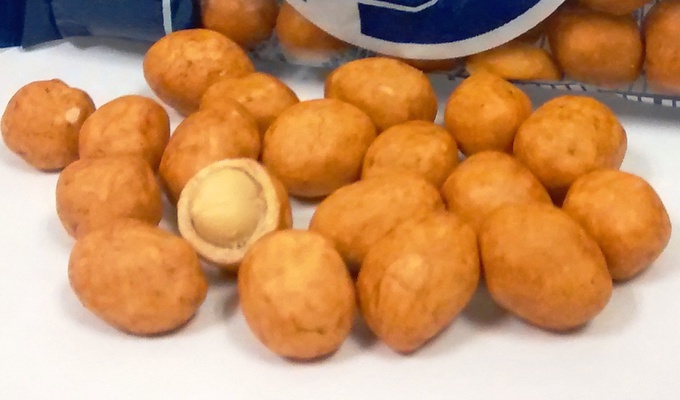
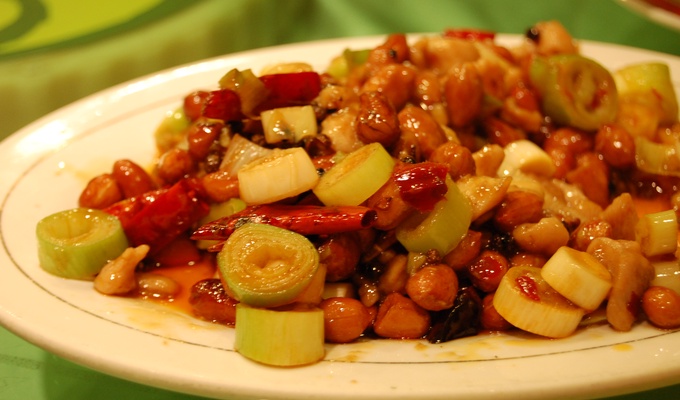
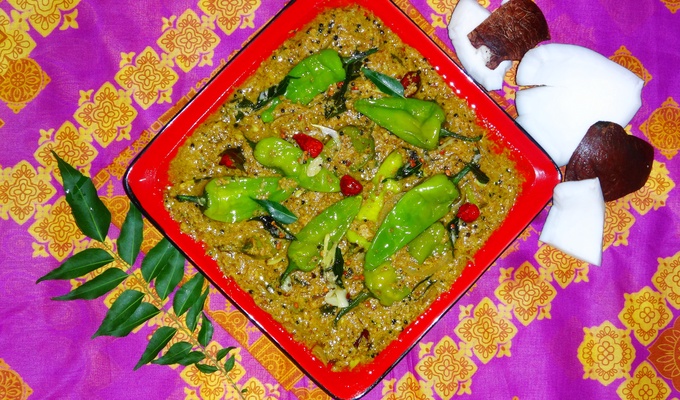
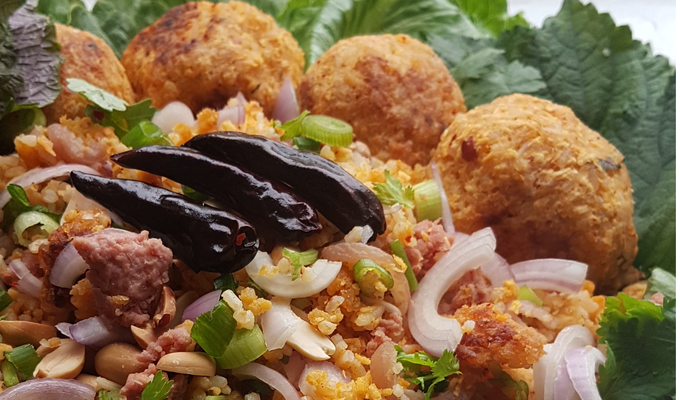
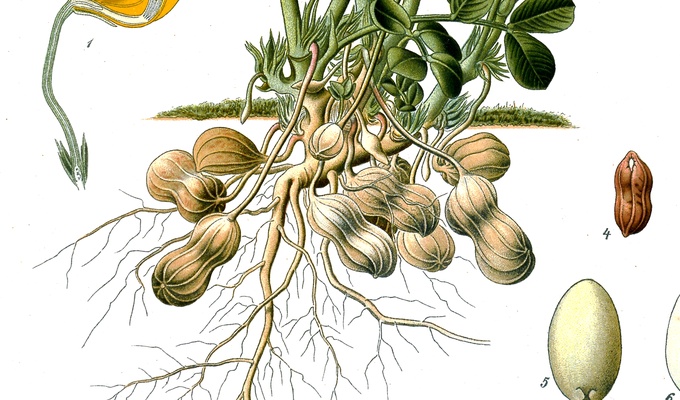
The peanut, also called groundnut, goober, pindar, or monkey nut, is an American legume. It is not a true nut, but because it has a similar taste and range of culinary uses, it is often classified as a nut. Note potential confusion with the American groundnut or "potato bean," which is unrelated.
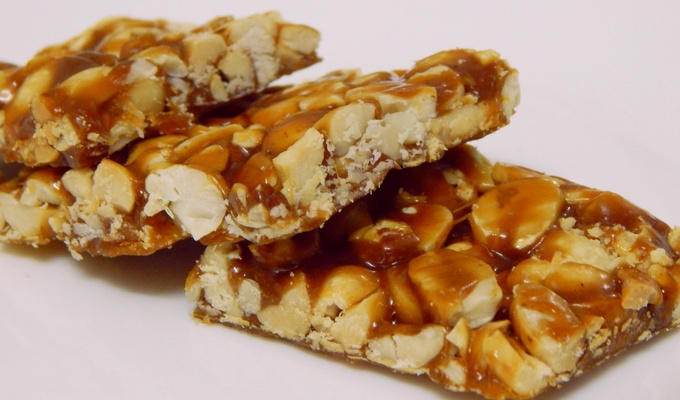
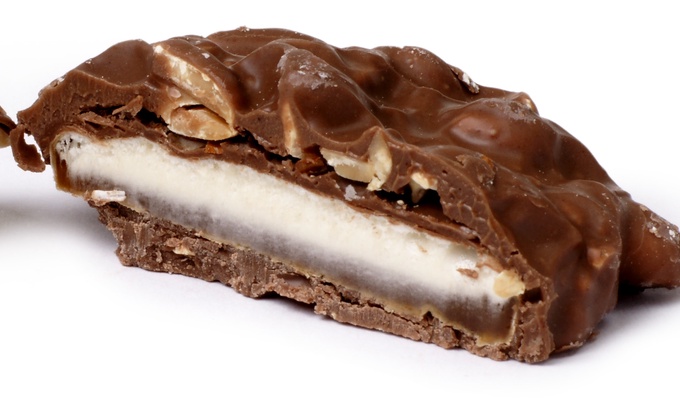
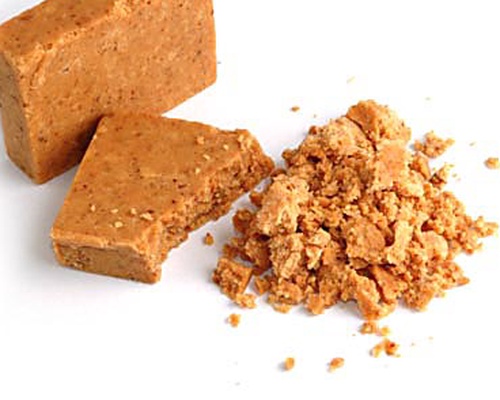
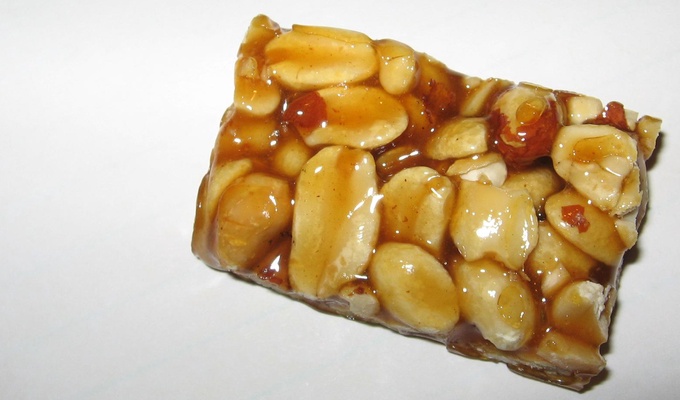
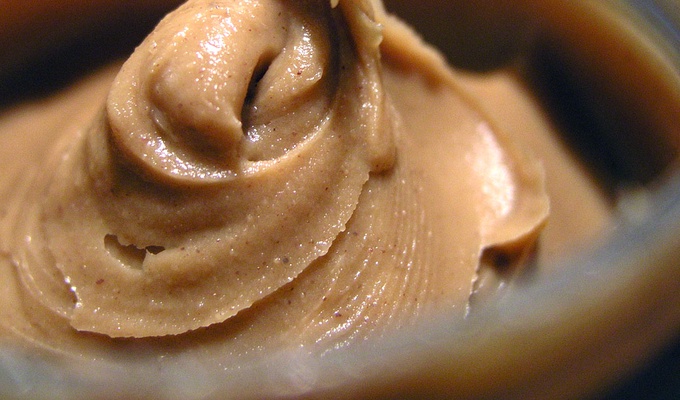
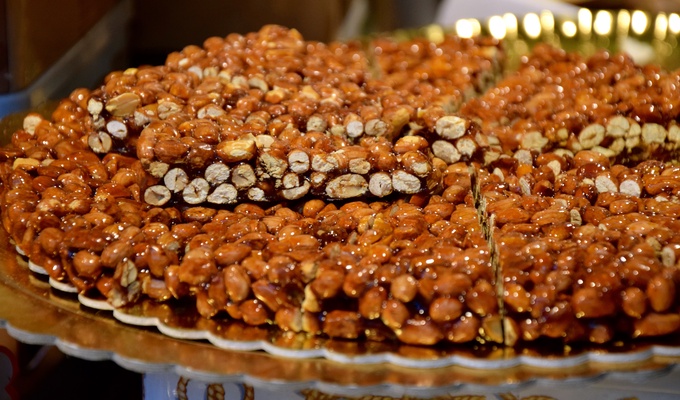
Peanuts have a wide range of uses in food. Whole roasted peanuts are popular as a snack food or as an ingredient in stir-fries and candies. Peanut oil has a very high smoke point and is therefore well-suited to deep frying. Peanut butter, made of finely ground peanuts, sometimes augmented with salt, emulsifiers, or sweeteners, is a popular sandwich filling, cracker topping, and ingredient in pastries and candies. Finely ground peanuts are used in sauces.
A relatively high number of people, estimated at between 0.6 and 1.2% of the United States population, report allergic reactions to peanut exposure. The range of allergic reactions is particularly severe, with anaphylactic shock from peanut allergy a leading cause of allergy-related death in children. This has led to a number of restrictions on the use of peanuts in public places, including schools, airplanes, and cafeterias. Proper control of peanuts and residue from peanut preparation is critical in any kitchen that will be serving the public, or a known person with peanut allergy.