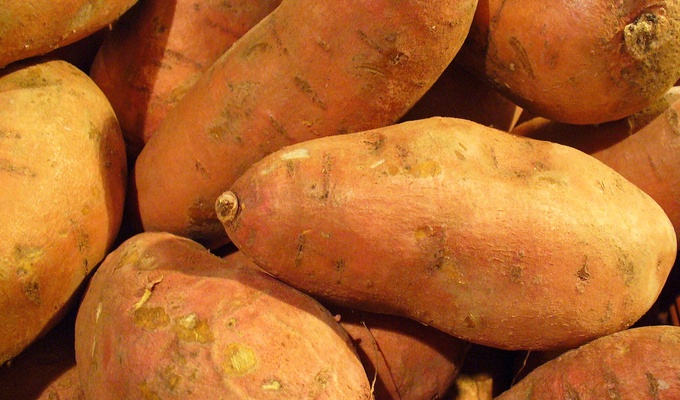The sweet potato is the large, sweet tuber of the Ipomoea batatas plant, and the name of the plant itself. It is native to the Americas, and spread throughout Polynesia prior to European contact, but is now cultivated worldwide.
The term kumara is used to refer to sweet potato in New Zealand, particularly in Māori culture. The word "kumara" comes from the Māori language, the language of the indigenous Polynesian people of New Zealand, and it has become the common term for sweet potato throughout the country. The kumara holds cultural significance in Māori traditions and was a staple crop in pre-European Māori agriculture. Different varieties of kumara are grown in New Zealand, and it remains an important part of the country's cuisine today.
In Japan, a variety of sweet potato called satsumaimo is preferred. These have a red-toned purple skin and off-white interior that turns white after cooking.
Sweet potatoes are often called "yam" in North America, despite being unrelated to Eurasian yam species. The naming convention arose from enslaved Africans who referred to the American crop as "yams", because of their similarity to the African plants they were familiar with.