Ground provisions is a term used in Caribbean cooking for foods that grow as roots or corms, or that grow off a tree as suckers, shoots, or vines. It also includes plantain and banana, which, despite growing as tree fruits, are prepared in a similar way as the other root vegetables.
They are often cooked and served as a side dish in local cuisine. Caribbean recipes will often simply call for ground provisions rather than specify specific vegetables.
Ground provisions are the main source of carbohydrates in the Caribbean diet, and traditionally were the most important staple crops of the region.
The major ground provisions are:
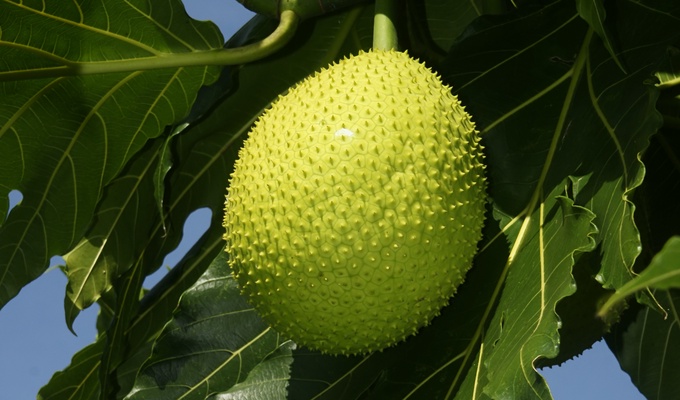
- Breadfruit
- Cassava (also called yuca or manioc). When dried, called tapioca.
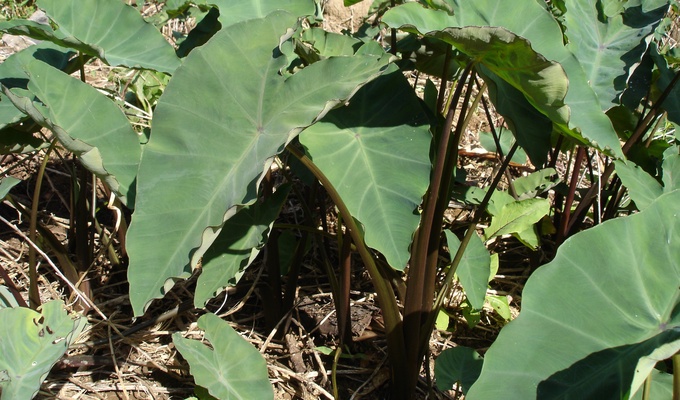
- Taro (called dasheen root).
- Eddo or eddoe, which is closely related to taro, but usually smaller.
- Malanga, also yautía and tannia, often confused with taro; malanga and taro are collectively called cocoyam.
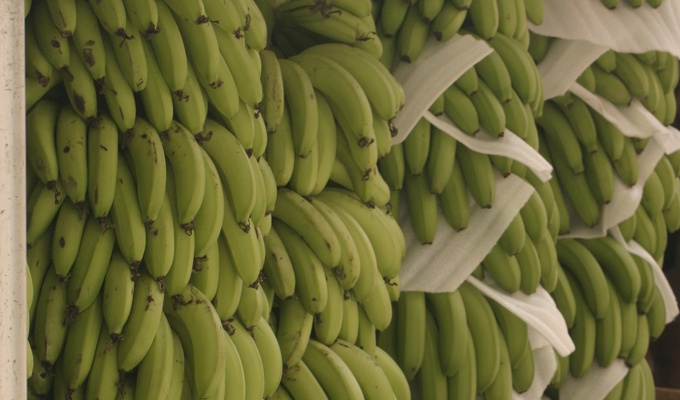
- Plantains, and to a lesser degree, bananas
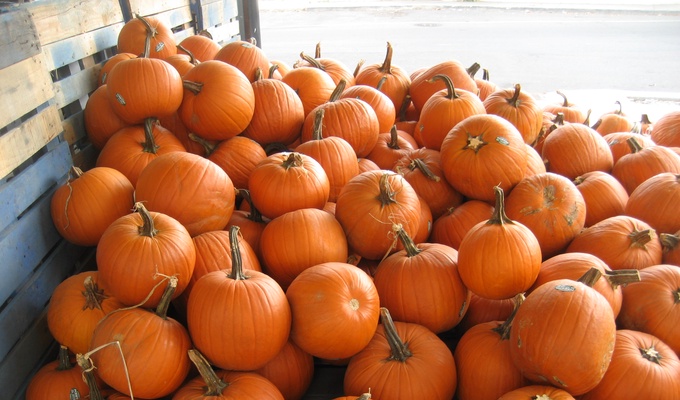
- Pumpkin
- Sweet potatoes, in the morning glory family; frequently misnamed as yams in the United States
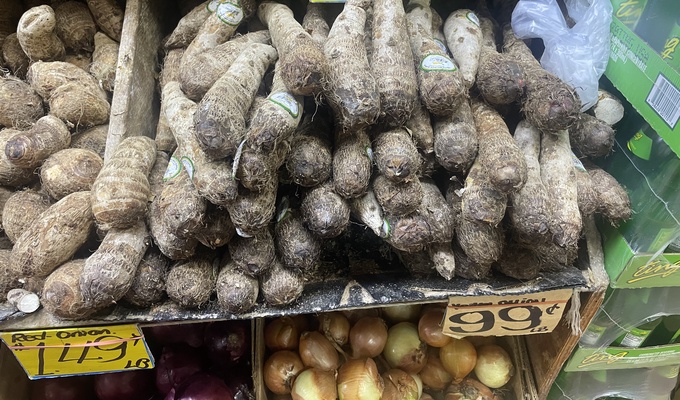
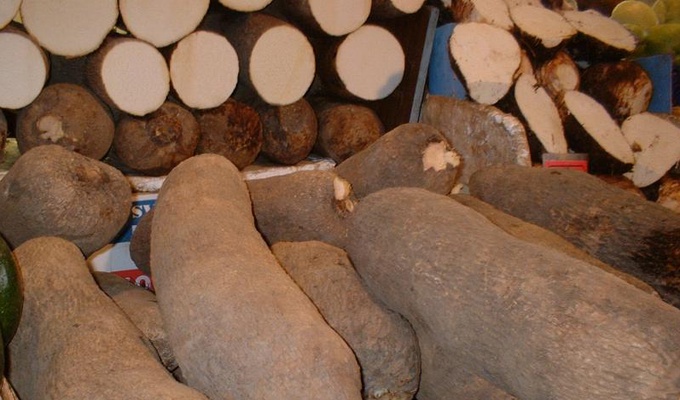
- Yams, including the true yams of the Americas, as well as imports from Asia and Africa